Company Biography
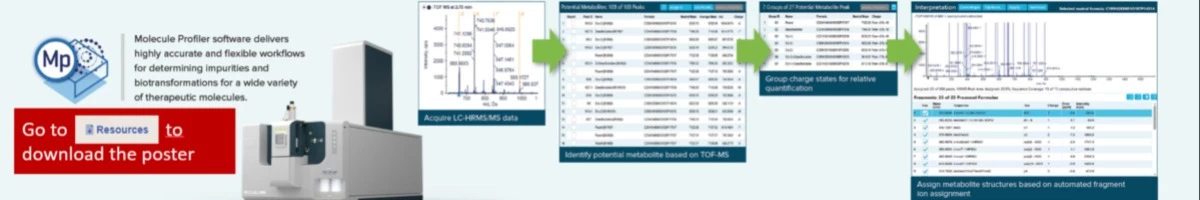
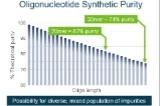
Synthetic oligonucleotides, including small interfering RNAs (siRNAs), antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and aptamers, continue to grow as a viable therapeutic modality. All of these classes utilize a serial synthesis for their production, which is prone to impurities that are multiplicative in nature. Many of these impurities can be isoelemental and thus almost impossible to fully characterize by a precursor ion only LC-MS workflow. Therefore, the need exists for a combined LC-MS and LC-MS/MS workflow to fully characterize the main product and impurities with high confidence. Unfortunately, the complexity of MS/MS spectra for oligonucleotides has made it difficult to develop an effective workflow solution including streamlined data reduction. Here, a novel ion trap (Zeno trap) is employed to achieve significantly improved MS/MS fragment ion coverage and oligonucleotide sequence coverage on a new LC-MS/MS QTOF system (ZenoTOF 7600 system, SCIEX). In addition, a highly automated software, which leverages MS, MS/MS and optical data, is utilized for impurity and biotransformation studies. A 2’-O-methoxyethyl phosphorothioated RNA (18-mer) and several n-X impurities at various concentrations were spiked into buffer. The samples were subjected to LC-MS/MS acquisition. The data were processed in the novel Molecule Profiler software against custom impurity libraries for oligonucleotides. MS1 results showed a very high level of agreement between intact isotope distributions and theoretical isotope models with excellent mass accuracies. Based on MS1 identification, a targeted MS/MS method was set up with and without the usage of the Zeno trap. Highly descriptive fragment ion spectra were generated. Matching data against in-silico information in the software allowed for detection and identification of spiked-in impurities down to a 0.1% spike. A significant enhancement of MS/MS data quality could be observed, resulting in higher coverage of consecutive residues when using the Zeno trap, due to increasing the duty cycle.
Contact Information
Team Members

Todd Stawicki
SCIEX
Presenter

Kerstin Pohl
SCIEX
Co-Author