Company Biography
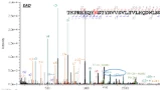
The glycosylation profile of biotherapeutics is quite heterogenous, and is a key area that requires multiple methodologies to ensure full characterization as the complexity can pose analytical problems. The CID-based mass spectrometry approach for peptide mapping has continued to have difficulty with glycopeptides as traditional fragmentation techniques do not allow for consistent identification and localization of glycans on peptides. Here, a newly developed dissociation technique that creates MS/MS fragment ions while maintaining the intact glycosylation was evaluated. A second technology called Zeno trap was used in conjunction to enhance the duty cycle for MS/MS fragment ions and improve the overall sensitivity and coverage of peptides. NISTmAb and trastuzumab, 2 humanized IgG1 mAbs, were prepared and digested with trypsin before injection into the LC-MS/MS system for peptide mapping. Data was acquired using data-dependent acquisition on a QTOF system (ZenoTOF 7600 system, SCIEX) with either CID or electron activated dissociation (EAD), a novel type of ExD. The resulting data from both types of acquisition was evaluated by comparing sequence coverage, peptide fragments, oxonium ions and peptide glycan fragments. While sequence coverage using CID and EAD was comparable, major differences were identified in glycosylated peptides. CID showed oxonium ions as being dominant in the spectra, while EAD showed a rich abundance of c- and z-ions, providing full coverage of the peptide backbone. Along with providing full peptide backbone coverage, EAD fragmentation included fragment ions with the intact glycosylation attached, allowing for unambiguous assignment of the location of this modification. This ability to assign location was not only identified on high abundant glycopeptides such as G0F-peptide, but also perpetuated to much lower abundant glycans such as Mannose 5, and the unambiguity of assignment was maintained because of the high-quality fragment ion spectra. Data derived from CID could not provide this level of information.
Contact Information
Team Members

Zoe Zhang
SCIEX
Presenter

Fang Wang
SCIEX
Co-Author

Jenny Albernese
SCIEX
Co-Author

Kerstin Pohl
SCIEX
Co-Author
